
As the internet progressed technologically so did its risks. The introduction of the revolutionary internet connection paved the way for a new category of crimes called cybercrimes. These included hacking attacks, identity thefts, fraud, and many more. The most recent risk that hit the World Wide Web is the “Ransomware“. Even though the Ransomware was invented back in the late 80’s yet a new version of it resurfaced a few days ago and it is being referred to as WannaCry.
What is it?
Ransomware is a more complicated and a vile form of malware that blocks victims from accessing their files on their PC by strongly encrypting them. After that the attacker requests a sum of money (Ransom) from the victim in order to send a decryption key. The most common form of payment requested is through Bitcoins as it is one of the most difficult methods to track. Other payment methods include iTunes and Amazon Gift Cards. This appears in a form of a pop-up message that appears on the victim’s computer screen.
Who Can Get Affected?
Ransomware attackers target both individuals and businesses as they do not have a particular selection patterns (hit anyone and everyone). The most common targeted operating system is Microsoft Windows, however, some Android devices as well have been infected. Even though businesses are targeted more than individuals, as they are more likely to pay, since encrypting their files can severely impact the business’s continuity. Yet, individual internet users are bound to this attack as well. In a matter of days, over 200,000 devices worldwide were hit.
How Can Victims Get Affected?
Ransomware penetrates the victim’s system in the same way a malware does and that is through the following methods:
- Emails with infected attachments
- Websites with infected links
- Security exploits in vulnerable software
- Drive-by downloads
- Infected links sent in SMS to mobile devices
Types of Ransomware
There are 4 main types of Ransomware, yet each type comes in countless different forms, and this is what made it difficult to fully exterminate it worldwide. Each form has a unique decryption key that differentiates it from the other and it can take a while to come up with all the possible keys. The 4 main types are as follows:
Encryption Ransomware
This type encrypts all the personal files on the computer (photos, videos, documents, etc.). Once they are encrypted a message appears in a form of a text file requesting the payment in order for a key to be sent to decrypt the files.
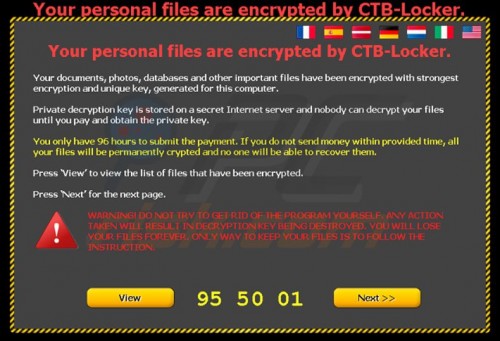
Lock Screen Ransomware – WinLocker
In this case the entire computer screen is locked making everything inaccessible by the user. The message here requesting the payment takes up the entire screen.

Master Boot Record (MBR) Ransomware
Here, the part of the computer hard drive responsible for booting up the operating system, is the one that’s affected. So the process of starting up the operating system is interrupted and instead a ransom request message appears.
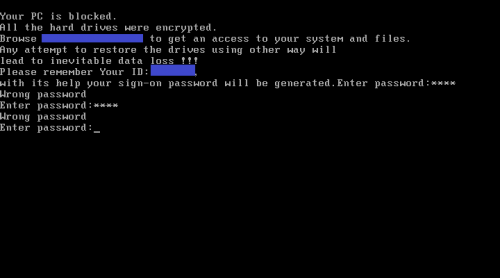
Ransomware Encrypting Web Servers
This Ransomware targets entire servers and encrypts the files on it. This is usually what happens in the case of businesses being attacked.
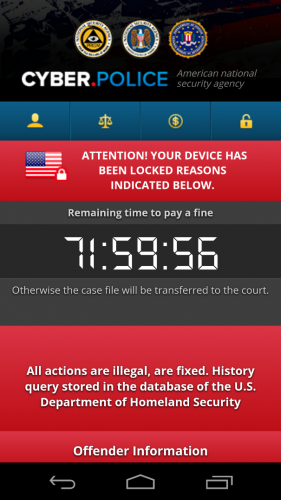
Mobile Device Ransomware
Mobile devices (mostly Android) are targeted through drive-by downloads or text messages (SMS) with infected links. Adding to that fake apps disguised in popular names like Adobe Flash or anti-virus apps.
How to Protect Yourself against Ransomware
Even though it is not possible to decrypt all forms of Ransomware yet, but you can still take measures to prevent such an attack. Here are a few ways to protect your computer against Ransomware attacks:
Backup
Always keep a regularly updated backup of your important files. This can either done on an external hard drive or to back up your data on any trusted online cloud (Google Drive, Dropbox, etc.)
Update Operating System
The older the version of Window your using (Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows Vista), the more vulnerable it will be to attacks such as Ransomware.
Use an Anti-Malware
There are some very reliable anti-malware applications (e.g. Malwarebytes) available and they will do a very good job in protecting your computer, only as long as you keep them up to date.
Avoid Suspicious Online Links
Try to avoid as much as possible clicking on suspicious links or accessing suspicious websites as this is a very popular gateway for Ransomware attackers.
Avoid Untrusted Email Attachments
Refrain from opening emails or attachments in emails that are from unknown or suspicious sources. Even if it is from a trusted source it is preferable to scan the attachment first using an updated anti-virus and/or anti-malware.
Install a Well-Trusted Ransomware Blocker
Ever since Ransomware attacks resurfaced and several online security companies have been developing and issuing reliable Ransomware blocker programs and are continuously updating them with new security measures. It is always safer to acquire one of them and regularly update it.
Close Risky Ports on Windows
If you are using Windows 7, Vista, XP, or 2000 then it is important, as an additional security measure, to close the ports; 445, 135, 138, and 139.
Use a Suitable VPN
Another good security measure is using a suitable VPN with strong online security measures. More details about how a VPN can protect you against Ransomware are found below.
How Can a VPN be Helpful?
The core purpose of a VPN is to boost your online security and keep your internet session completely private. It keeps your online identity anonymous. This is because when you connect to a VPN service all your internet traffic is highly encrypted and passes through one of the servers operated by the VPN provider instead of that of the ISP. This server provides you with a different IP address than your true one. At this point it becomes more difficult for cyber criminals to track your true online identity and try to attack your device using Ransomware.
A highly recommended VPN here would be BVPN as it has extremely competitive online security measures. From a 256-bit encryption, to secure its network of over 20 worldwide server locations, to multiple advanced and unique security protocols (OpenVPN, L2TP/IPSec, SSTP, and its very own powerful Smoke Tunnel).

Conclusion
The internet has become a risky place, yet if we think about it, things like the Ransomware attack are what continuously remind us to stay secure and continuously update both our online and offline security measures. Some forms of Ransomware are more dangerous than others but as long as we keep regular backups of our important files and take all the security precautions mentioned above, we should be fine.


